Cement Roads Get Eco-Friendly Upgrade with Built-in Recharge Systems
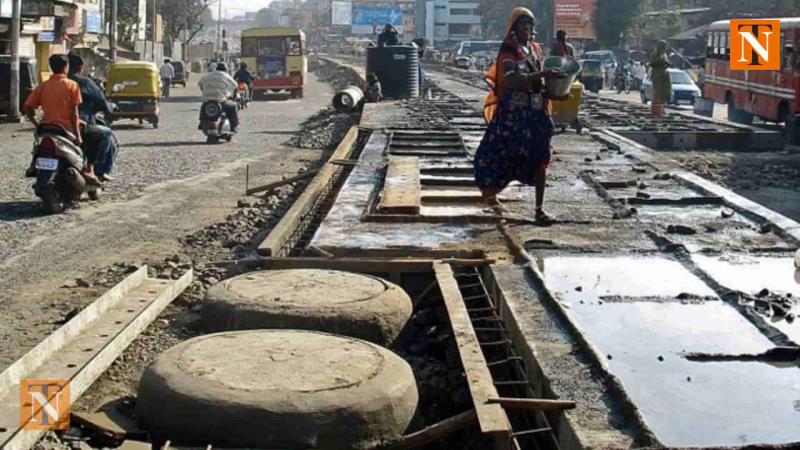

Nagpur, India: In a new step towards water conservation, the Nagpur Municipal Corporation (NMC) is now constructing groundwater recharge pits along with new cement roads. This effort, part of Phase-IV of the cement road development project, is aimed at harvesting rainwater, reducing waterlogging, and helping to improve the city’s groundwater levels.
So far, 11 recharge pits have been built in Khamla along Cement Roads 3 and 4 under Package 2. Another five pit locations have been marked near Dhantoli Garden. Similar work is also being taken up in other areas like Ashi Nagar.
Each recharge pit includes a 300 mm wide bore drilled 20 metres deep. A chamber is built at the bottom and filled with layers of sand, charcoal, and gravel to filter rainwater. The clean water then seeps into the ground, helping recharge the water table. These pits are connected to roadside drains and stormwater lines, so that rainwater doesn’t go to waste or cause flooding.
To prevent blockages, iron grates are placed over the pits to keep out debris. The NMC also has a long-term maintenance plan to ensure the system keeps working properly.
A total of 147 recharge pits will be installed along 33 cement roads covering over 23 km. The work is being done by M/s RM Dayaramani, who will also maintain the system for the next 10 years.
Recently, Municipal Commissioner Dr Abhijeet Chaudhari visited sites near Sneh Nagar and Joggers Park, along with senior officials. He was satisfied with the work and has suggested a one-month trial to monitor how well the system works. Chief Engineer Leena Upadhyay said additional features like trash filters will be added to make the system more effective.
This project shows a smart and sustainable way of building city roads—helping not only in transport but also in saving water for the future.


-t-thumb.jpeg)





-t-thumb.jpeg)

-t-thumb.jpeg)
